What to Expect During a Hearing Test
Have you ever had a hearing test? For many, hearing assessments aren’t a
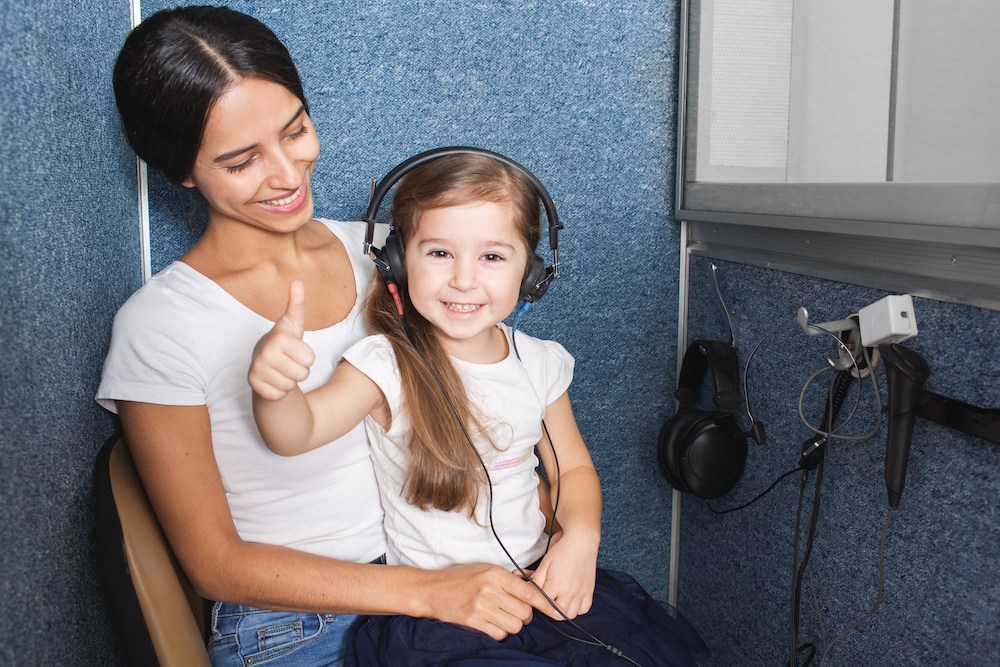
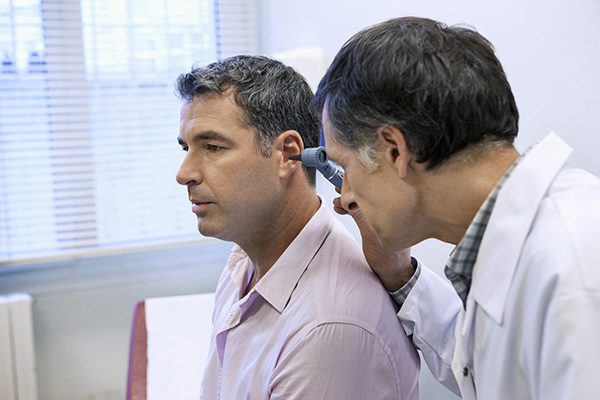

Have you ever had a hearing test? For many, hearing assessments aren’t a
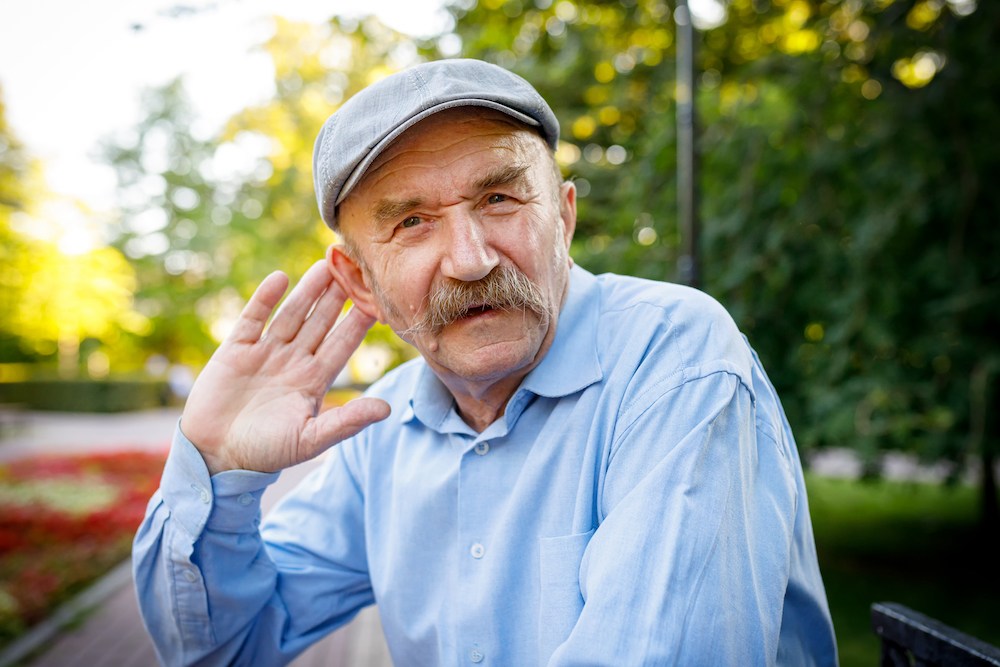

As people get older, it’s common for their hearing to change over time.
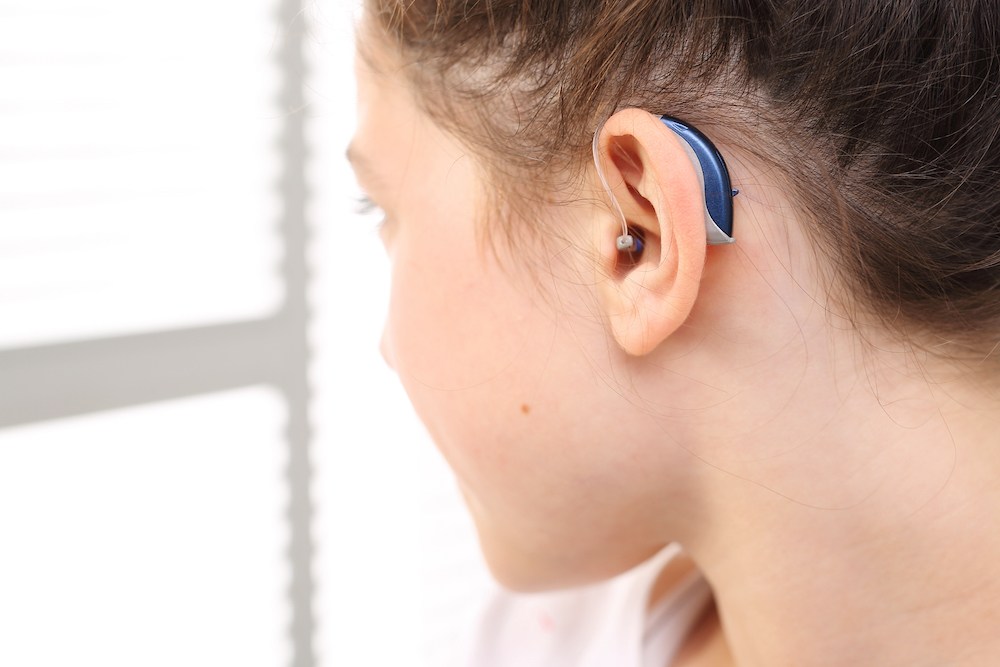

Are you finding it hard to stay productive at work because of hearing